Distinguish Between Ideal and Real Stoichiometric Calculations
No intermolecular attraction force. Difference between Ideal gas and Real gas.

Ideal Stoichiometric Calculations Ppt Download
It really exists in the environment.
. Solutions ideal solutions follow Raoults Law which in practice only applies to very very dilute solutions. Almost all stoichiometric problems can be solved in just four simple steps. Solving any reaction stoichiometry problem must begin with a balanced equation.
However stoichiometric calculations will tell you the maximum amount. The gases that can be examined perfectly with the ideal gas law are referred to as ideal gases however most real gases are rarely ideal when it comes to their properties. Ideal in which all reactants are completely converted into products.
Distinguish between ideal and real gas. Chapter 9 Section 2 covers Stoichiometric Calculations including mole to mole mole to mass mass to mole and mass to mass examples. Under ideal conditions all the reactants are completely converted into the products.
Radiation in an ideal blackbody the radiation is in thermal equilibrium with the solid. 124 Ideal Gas. It is defined as the sum of the atomic weights of each atom present in the molecule of the substance.
What is the difference between real transformer and ideal transformer. Calculate the amount of gas at any specified conditions of pressure volume and temperature. Chemical equations help us plan the amounts of reactants to use in a chemical.
Distinguish between ideal and real stoichometry calculations. A practical pendulum is one that is readily available and reliable made from things you have right now and are available to use. Stoichiometric coefficient or stoichiometric number is the number of molecules that participate in the reaction.
Distinguish between ideal and real stoichiometric calculations. Avogadros number is defined as the number of particles present in one. Limiting reactant limits the amount of the other reactant that can combine and the amount of product that can form in a chemical reaction.
Calculations involving the mass relationships of elements in compounds. Stoichiometric Calculations are Based on Chemical Formulas. Excess reactant is the substance that is not used up completely in a.
An Ideal pendulum is ones that would be the first choice if you could choose all the materials ideal materials. Real stoichiometry calculations account for actual conditions. You need relatively high temperatures and low pressuers.
Many real reactions proceed in a such a way that not all reactants are converted to products. For example we can calculate the formula mass of Na 2 S as 2 23 1 32 78. The stoichiometric coefficient is basically the number present in front of atoms molecules or ions.
The ideal gas law denotes a particular equation that can be used to calculate the variables of volume amount pressure and temperature when examining the properties of gases. Elastic collision of particles. Gases ideal conditions occur when the ideal gas law is follows.
Using the mole ratio calculate the moles of substance yielded by the reaction. If you look at any balanced reaction you will notice that there are an equal number of elements on both sides of the equation. There is no leakage flux in an ideal transformer.
There are basically 4 major differences - 1. Ideal Stoichiometric Calculations A balanced chemical equation is the key step in all stoichiometric calculations because the mole ratio is obtained directly from it. What is the difference between ideal and practical pendulum.
Stoichiometric calculations are so important in the industrial production of chemical substances because through these calculations you are able to derive many things involved in the essence of that branches intentions. Now youre ready to use what you know about conversion factors to solve some stoichiometric problems in chemistry. Reaction that takes place under ideal conditions.
Convert units of a given substance to moles. Non-elastic collisions between particles. Flinn Quick Freeze in folder 8.
Lets learn some terms used in Stoichiometry first. The difference is ideal are. Does not really exists in the environment and is a hypothetical gas.
For example formula mass of Na 2 S is calculated as 2 23 1 32 78. Ideal tells the most possible amount of products and real is the actual amount of products what is the difference between limiting and excess reactant in a chemical equation. The windings both primary and secondary of an ideal transformer are considered to have zero resistance hence the transformer is lossless.
-Introduction to Stoichiometry -Ideal Stoichiometric Calculations -Limiting Reactants and Percentage Yield. Stoichiometric Calculations are mostly based on chemical formulas. This week students will perform classic experiments to measure Ideal Gas Law Constant R and find Absolute Zero.
It is the sum of the atomic weights of the various atoms present in the molecule of the substance.

Ideal Stoichiometric Calculations Ppt Download

Flow Chart For Stoichiometry Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Dimensional Analysis

Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Pages Intro To Stoichiometry All Stoichiometric Calculations Start With A To Solve You Ppt Download

Unit 6 Stoichiometry Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Chapter 9

Stoichiometric Calculations Youtube

Unit 6 Stoichiometry Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Chapter 9

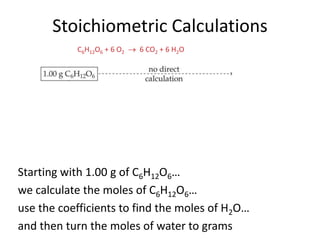
Chapter 9 2 Ideal Stoichiometric Calculations Ppt Download

Stoichiometric Calculations Ppt Download

Unit 6 Stoichiometry Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Chapter 9
Ppt Stoichiometric Calculations Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 2524699

Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Pages Intro To Stoichiometry All Stoichiometric Calculations Start With A To Solve You Ppt Download

Solved Distinguish Between Ideal And Real Stoichiometric Calculations

Unit 6 Stoichiometry Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Chapter 9

Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Pages Intro To Stoichiometry All Stoichiometric Calculations Start With A To Solve You Ppt Download

Unit 6 Stoichiometry Chapter 9 Stoichiometry Chapter 9
Stoichiometric Calculations Mole Ratio Easy Learning Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment